For plastic injection mold design, one of the most important factors is how and where the gate should be located. As the mold opening, the gate is where the molten plastic flows into the final part. It serves as the boundary between the part and the scrap, so its location, size, and shape play an important role in how everything should be constructed, from structural integrity to exterior appearance of the finished product.Below is gate type we often choose:
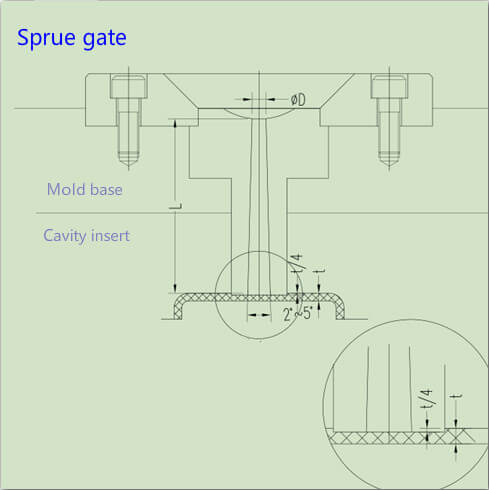
Direct Gate(Sprue gate):
Pros:
1. Little pressure loss;
2. Easy preparation.
Cons:
1. High stress around the gate;
2. Gate (runner) needs to be trimmed manually;
3. Obvious gate scars will be left on the surface.
Application:
1. Suitable for production of large and deep barrel-shaped plastic parts. However, warping can easily occur due to contractibility and stress when applied on shallow and flat plastic parts.
2,For plastic parts that do not allow gate marks on the exterior, the gate can be designed on the inner surface of the parts.
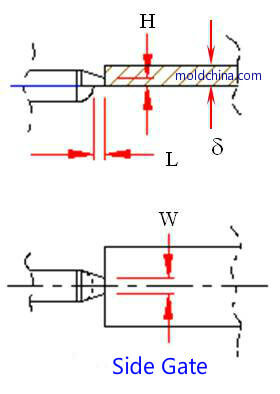
Side Gate:
Pros:
1. Simple structure, easy processing;
2. Easier to remove the gate.
Cons:
1. Automatic separation of the part and the gate is not allowed;
2. Gate marks are easily left on the plastic part.
Parameters:
1. Gate width W = (1.5~5.0)mm. Usually W = 2H, which may be appropriately increased for large and transparent plastic parts.
2. Height H = (0.5~1.5)mm. Specifically speaking, usually H = (0.4~0.6)d for commonly seen ABS and HIPS. Among them, d refers to the basic wall thickness of the plastic part; H = (0.6~0.8)d for materials with poor fluidity, like PC and PMMA; the suggested gate height for POM and PA is H = (0.6~0.8)d, so as to help avoid shrink marks and wrinkles by guaranteeing sufficient pressure holding, because though these materials possess good fluidity, they become solid very fast with larger contractibility; for materials like PE and PP, gate height H = (0.4~ 0.5)d, because the small-sized gate is helpful for molten plastic shear thinning, thus reducing stickiness.
Application:
1. Suitable for production of plastic parts of various shapes, but it is will not be selected for slender barrel-shaped parts.
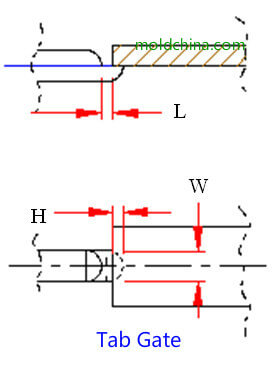
Tab Gate:
Pros:
1. It is a form evolved form the side gate, so it shares the various advantages of the side gate;
2. It is a typical impingement gate that can effectively prevent molten plastic jetting.
Cons:
1. Automatic separation of the part and the gate is not allowed;
2. Obvious gate scars are easily left on the surface.
Parameters:
Refer to the side gate parameters for application.
Application:
Suitable for flat plastic parts that impose requirements on surface finish.
Fan Gate:
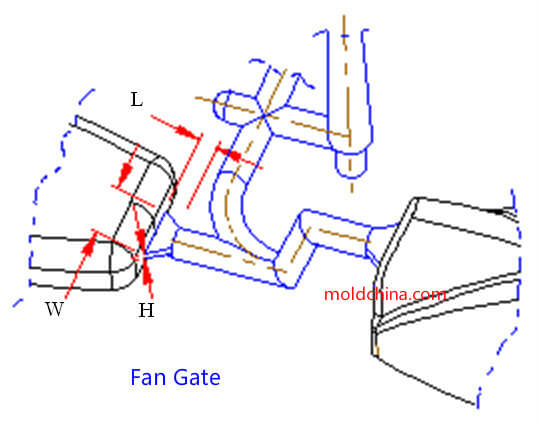
Pros:
1. The horizontal distribution of the molten plastic is more uniform when passing through the gate, helpful for reduction of plastic part stress;
2. Lower the possibility of air getting into the cavity, to avoid the occurrence of defects, like silver lines and bubbles, etc.
Cons:
1. Automatic separation of the part and the gate is not allowed;
2. Long gate marks are left on the edge of the plastic part, which need to be flattened by a tool.
Parameters:
1. The commonly used height H = (0.25~1.60) mm;
2. Width W = 8.00 mm to ¼ of the cavity width at the gate end.
3. The section area of the gate should be larger than that of the sub-runner.
Application:
Usually used for production of wide but thin plastic parts, as well as transparent plastic parts and those with poor fluidity, like PC and PMMA, etc.
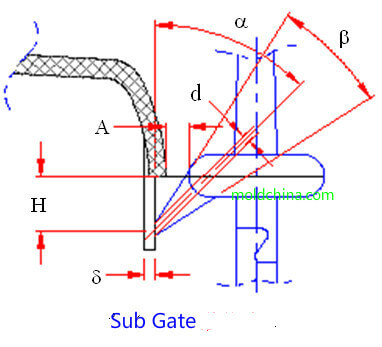
Submarine Gate:
Pros:
1. Flexible choices of gate location;
Automatic separation of the part and the gate is allowed;
3. Smaller gate marks;
4. Applicable for both 2-plate and 3-plate molds.
Cons:
1. Plastic powder is easily dragged at the gate position;
2. Stress mark is easily created at water entry;
3. Plastic films need to be sheared manually;
4. Great pressure loss from the gate to the cavity.
Parameters:
1. Gate diameter d = 0.8~1.5mm;
2. The plastic flow direction and the vertical direction form an angle a between 30°and 60°;
3. The taper b is between 15° and 25°;
4. Distance to the cavity A = (1.5~3.0)mm.
Application:
Suitable for plastic parts that do not allow exposed gate marks on the exterior. For a multi cavity mold, the resistances from the gate to each cavity should be kept as close as possible, so as to avoid viscous flow and obtain better flow balance.
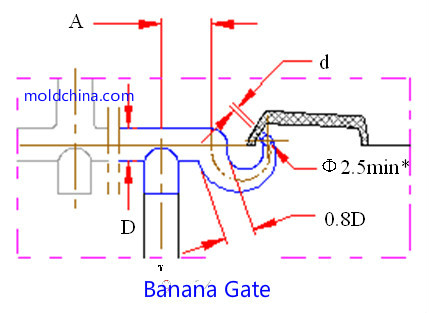
Banana Gate:
Pros:
1. Automatic separation of the part and the gate is allowed;
2. The gate area does not need additional processing;
3. No gate marks will be left on the exterior of the plastic parts.
Cons:
1. Stress marks may show on the surface;
2. Complicated processing;
3. Easily broken and thus blocking the gate if not appropriately designed.
Parameters:
1. Gate diameter at water entry end d = (Φ0.8~Φ1.2) mm, length = (1.0~1.2) mm;
2. A = approx. 2.5D;
3. Φ2.5min* refers to the gradual transition from the large end 0.8D to the small end Φ2.5.
Application:
Normally used for ABS and HIPS, suitable for neither crystalline materials like POM and PBT, nor high-rigidity materials like PC and PMMA, so as to avoid the curvy runner from being broken and thus blocking the gate.
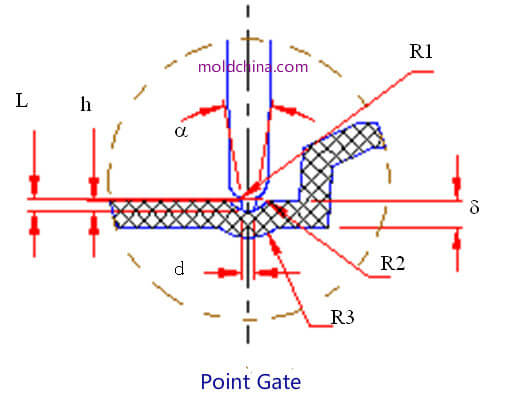
Point Gate:
Pros:
1. Flexible choices of gate location;
2. Automatic separation of the part and the gate is allowed;
3. Smaller gate marks;
4. Low stress around the gate.
Cons:
1. High injection pressure;
2. Complicated structure, usually employing the 3-plate structure.
Parameters:
1. Usually the gate diameter d = (0.8~1.5) mm;
3.The gate length L = (0.8~1.2) mm;
4. To help pull the gate broken from the root, a taper should be set for the gate, a = approx. 15°~20°;
the gate and the runner are joined by arc R1 to ensure that the plastic part is not damaged when pulling the point gate broken; R2 = (1.5~2.0) mm; R3 = (2.5~3.0) mm; height h = (0.6~0.8) mm.
Application:
Usually used for the production of large plates and bottom cases. The proper distribution of gate can help reduce the flow distance of molten plastic and thus guarantee satisfactory distribution of melting marks; also able to be used for production of long barrel-shaped plastic parts to improve ventilation.
All copyright reserved by injection molding manufacturer Sositar Mould